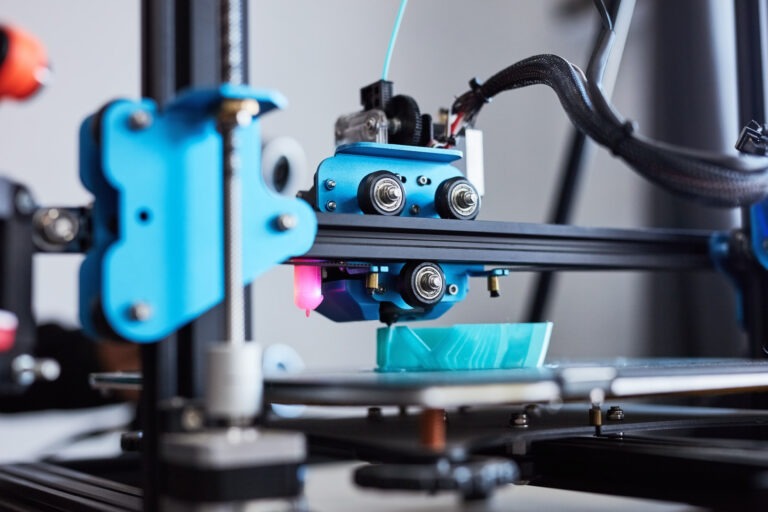
2024 has seen additive manufacturing (3D printing) evolve beyond rapid prototyping to become a crucial tool for end-use manufacturing.
The automotive and aerospace sectors have been leaders in this field, with companies like Ford, Boeing, and GE integrating additive manufacturing into their production lines.
Ford’s use of additive manufacturing to produce lightweight, durable components for electric vehicles (EVs) helped the company reduce part costs and production times, giving it a competitive edge in the growing EV market.
Meanwhile, Boeing has taken additive manufacturing to new heights, with the company printing metal parts for its airplanes.
By using additive manufacturing technology, Boeing has reduced material waste and sped up the production process.
In fact, additive manufacturing accounted for over 10% of the parts in some of Boeing’s new aircraft models in 2024.
… And while Boeing has had some difficulties recently, their use of additive manufacturing has helped them make a significant leap forward in the adoption of additive manufacturing.
In addition, GE continues to leverage additive manufacturing to revolutionize its product development and manufacturing processes.
The company uses 3D printing technology to produce complex, lightweight components with greater precision and efficiency, particularly in industries such as aerospace, energy, and healthcare.
GE has focused on creating advanced metal parts, including turbine blades and fuel nozzles for aircraft engines, reducing production time and material waste.
Additive manufacturing also allows for customization, enabling GE to better meet the specific needs of its customers.
By incorporating additive manufacturing into its operations, GE is improving its ability to innovate faster, reduce costs, and enhance sustainability.
These advancements position the company to stay competitive in an increasingly dynamic market while preparing for future technological demands, where digital and additive capabilities will be critical for continued growth and efficiency.